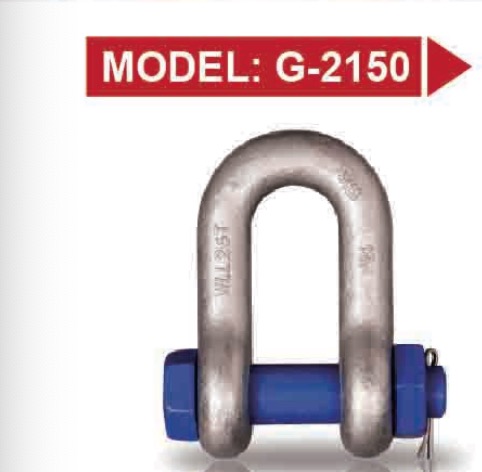
Introduction
In the world of rigging, lifting, and securing loads, the bolt type anchor shackle is a critical component used across multiple industries. Known for its strength, durability, and reliability, this type of shackle is commonly used where safety and load security are paramount. The bolt type anchor shackle differs from other shackles (like screw pin shackles) due to its bolt-and-nut design, which provides a more secure fastening mechanism. This article will examine the structure, usage methods, and common real-world scenarios where bolt type anchor shackles are employed.
1. Understanding the Bolt Type Anchor Shackle
1.1 Structure
A bolt type anchor shackle typically consists of the following components:
- Body (Bow or Anchor shape): A U-shaped body with a wider bow, which allows for multidirectional loading.
- Bolt: A threaded pin that passes through the ends of the body.
- Nut: A hexagonal nut that secures the bolt in place.
- Cotter Pin (or Split Pin): An additional safety mechanism that locks the nut and prevents accidental loosening.
This combination ensures the bolt remains securely fastened even under dynamic loads or vibration-heavy conditions, which is one of the major advantages over simpler screw pin shackles.
1.2 Materials and Coatings
Bolt type anchor shackles are typically made from high-strength forged steel, galvanized steel, or stainless steel. The surface can be hot-dip galvanized, electroplated, or painted for corrosion resistance depending on the intended environment.
2. Usage Methods of Bolt Type Anchor Shackles
Proper usage is critical for ensuring both operational effectiveness and safety. The following outlines best practices and usage methods.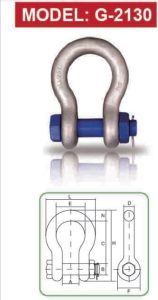
2.1 Load Alignment
The shackle should be aligned properly with the load:
- The load should be centered in the bow portion of the shackle.
- Avoid side loading, which can significantly reduce the shackle’s working load limit (WLL).
- The pin (bolt) should bear the load in straight-line applications.
2.2 Installation Procedure
Here’s how a bolt type anchor shackle should be properly installed:
- Inspect the shackle for any visible damage, deformation, or corrosion.
- Insert the bolt through the shackle’s ears.
- Tighten the nut to ensure a firm fit against the ears of the shackle.
- Insert the cotter pin through the hole in the bolt to lock the nut in place.
- Bend the legs of the cotter pin to secure it and prevent accidental removal.
This multi-layered locking mechanism prevents the pin from backing out under vibrations or shifting loads.
2.3 Regular Inspection and Maintenance
- Daily checks are recommended in high-use environments.
- Ensure the nut and cotter pin are intact and secure.
- Check for deformation, wear, or cracks in the shackle body or pin.
- Replace shackles if any component is missing or damaged.
2.4 Working Load Limit (WLL) Considerations
Each shackle comes with a clearly marked WLL. It’s critical never to exceed this limit. In multi-leg lifting slings, the WLL must account for load angle and distribution, which may significantly reduce the effective capacity of the shackle.
3. Scenarios of Bolt Type Anchor Shackle Usage
Bolt type anchor shackles find application across a wide spectrum of industries. Below are key scenarios:
3.1 Construction and Infrastructure
In heavy construction, bolt type anchor shackles are indispensable in:
- Lifting and rigging operations involving steel beams, prefabricated panels, or concrete blocks.
- Crane operations where the secure lifting of heavy components requires stable shackles.
- Tower assembly or bridge building, where vibration and multidirectional loading are concerns—making bolt-type shackles ideal due to their secure locking mechanism.
In such applications, safety regulations often mandate the use of bolt type shackles over screw pin variants.
3.2 Offshore and Marine Operations
Due to the harsh conditions and constant movement in offshore environments, bolt type anchor shackles are preferred for:
- Mooring lines where continuous wave action can loosen less secure fasteners.
- Lifting equipment on oil rigs, where reliability under dynamic loads is essential.
- Towing operations involving barges and marine vessels.
Galvanized or stainless steel versions are especially valued for their corrosion resistance in saltwater environments.
3.3 Mining and Earthmoving Equipment
Bolt type anchor shackles are frequently used in:
- Securing hoist chains and slings to massive earthmoving equipment.
- Transporting mining components, where load security is critical.
- Situations involving high vibration, where screw pins might work loose, but bolt types remain secure.
Their robust construction and locking mechanism prevent failures in rugged, high-vibration settings.
3.4 Industrial Manufacturing
In large-scale manufacturing plants, shackles are vital in:
- Assembly line hoisting of engines, machinery, or other large parts.
- Material handling systems that require secure and repeatable lifting.
- Automated gantry systems, where frequent loading and unloading demand secure but removable shackles.
The ability to safely leave the shackle in place over longer periods makes the bolt type especially suitable.
3.5 Entertainment and Stage Rigging
Though less obvious, bolt type shackles also appear in stage production:
- Securing trusses and rigging for lights, speakers, or backdrops.
- Overhead suspension of stage elements, where audience safety is a top concern.
- Outdoor concerts where environmental conditions may cause less secure shackles to loosen over time.
Due to the public safety implications, bolt type anchor shackles are often required in these scenarios.
3.6 Transport and Logistics
In the transport industry, particularly with heavy or oversized loads, bolt type shackles are used for:
- Securing cargo to flatbed trailers.
- Attaching winches or tie-downs to heavy machinery.
- Situations involving extended transit periods, where long-term security is necessary.
The bolt and cotter pin configuration ensures that road vibrations or shifting cargo don’t compromise the integrity of the attachment.
4. Advantages Over Other Shackle Types
The bolt type anchor shackle offers several distinct advantages:
- Enhanced security: The combination of bolt, nut, and cotter pin makes accidental disengagement highly unlikely.
- Long-term use: Unlike screw pin shackles, which can loosen over time, bolt type shackles are suitable for permanent or semi-permanent installations.
- Versatility: Suitable for lifting, towing, tie-downs, and suspension.
- Compliance with safety regulations: Often required by OSHA, ANSI, and other regulatory bodies in critical applications.
5. Limitations and Cautions
Despite their many strengths, bolt type anchor shackles do have some limitations:
- Time-consuming installation: Compared to screw pin shackles, the installation and removal process takes longer.
- Not ideal for rapid deployment: In situations where shackles must be frequently attached and detached, screw pin shackles may be more convenient.
- Misuse risks: Improper installation (e.g., omitting the cotter pin) can negate the security benefits.
- Environmental impact on materials: In corrosive environments, regular inspection and appropriate material choice (such as stainless steel) are essential.
6. Safety and Standards
Bolt type anchor shackles are designed and manufactured under specific standards such as:
- ASME B30.26 – Rigging Hardware
- Crosby or equivalent manufacturer guidelines
- EN 13889 – European standard for forged shackles
- BS 3032 – British standard
These standards define the mechanical properties, testing methods, and required markings, such as:
- Working Load Limit (WLL)
- Manufacturer identification
- Material grade
- CE or other certification marks
Users must ensure that shackles meet applicable standards for their region and industry.
Conclusion
Bolt type anchor shackles are a foundational component of safe and effective rigging, lifting, and securing systems. Their robust design and triple-locking mechanism make them ideally suited for environments where reliability and safety are non-negotiable. From construction sites to offshore oil rigs, from factory floors to entertainment stages, these shackles play a vital role in ensuring loads are safely managed under varying conditions.
While they are not always the quickest to install, the bolt type anchor shackle’s enduring security makes it the go-to choice in many high-stakes applications. By understanding their proper use, limitations, and scenarios for deployment, users can maximize both safety and operational efficiency. Whether for a single critical lift or a permanent installation in harsh environments, bolt type anchor shackles remain a cornerstone of modern load handling technology.

